- 27th Mar, 2024
- Rohit M.
What is Cybersecurity - Everything You Need to Know!
19th Sep, 2023 | Aarav P.
- Cybersecurity

In today's digital age, where our lives are intricately intertwined with technology, the term "cybersecurity" has become increasingly important. This article provides an in-depth exploration of cybersecurity, encompassing its definition, significance, core principles, layers, and various types.
With alarming statistics highlighting the ever-growing threat landscape, understanding and implementing robust cybersecurity measures is not just an option but a necessity.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practise of preventing theft, damage, or unauthorised access to computer systems, networks, and data. It encompasses a wide range of strategies, technologies, and practices designed to safeguard digital assets from cyber threats. These threats can include malicious attacks, hacking attempts, phishing attacks, and more.
The purpose of cybersecurity is to reduce risks and minimise the impact of cyber threats like data breaches, financial losses, and reputational harm. It involves employing a proactive strategy to identify vulnerabilities, protect against threats, detect breaches, respond to incidents, and recover from attacks.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is critical in today's interconnected world for protecting our data, privacy, and the basic foundations of our digital society. Cyber threats have become more complex and prevalent with the rapid rise of the internet and technology.
Let's look at some statistics that demonstrate the significance of cybersecurity.
1. Escalating Cyberattacks
A report from Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that by the year 2025, cybercrime is projected to incur a global annual cost of $10.5 trillion.
These staggering numbers underscore the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures to combat the escalating threats.
2. Expanding the Attack Surface
The attack surface is expanding with the development of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, cloud services, and remote work. As the attack surface grows, so does the potential for vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
In fact, the tech jury reports that there will be 27 billion IoT devices by 2025, creating a vast attack landscape.
3. Evolving Hacker Capabilities
Hackers are continuously improving their skills and tools. They employ advanced techniques, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to launch highly targeted and sophisticated attacks. These cybercriminals are well-organised and well-funded, making them formidable adversaries.
4. Data Breach and Privacy Concerns
Data breaches have become a common occurrence, compromising sensitive information and undermining trust in organisations. Such breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
The Three C's of Cybersecurity
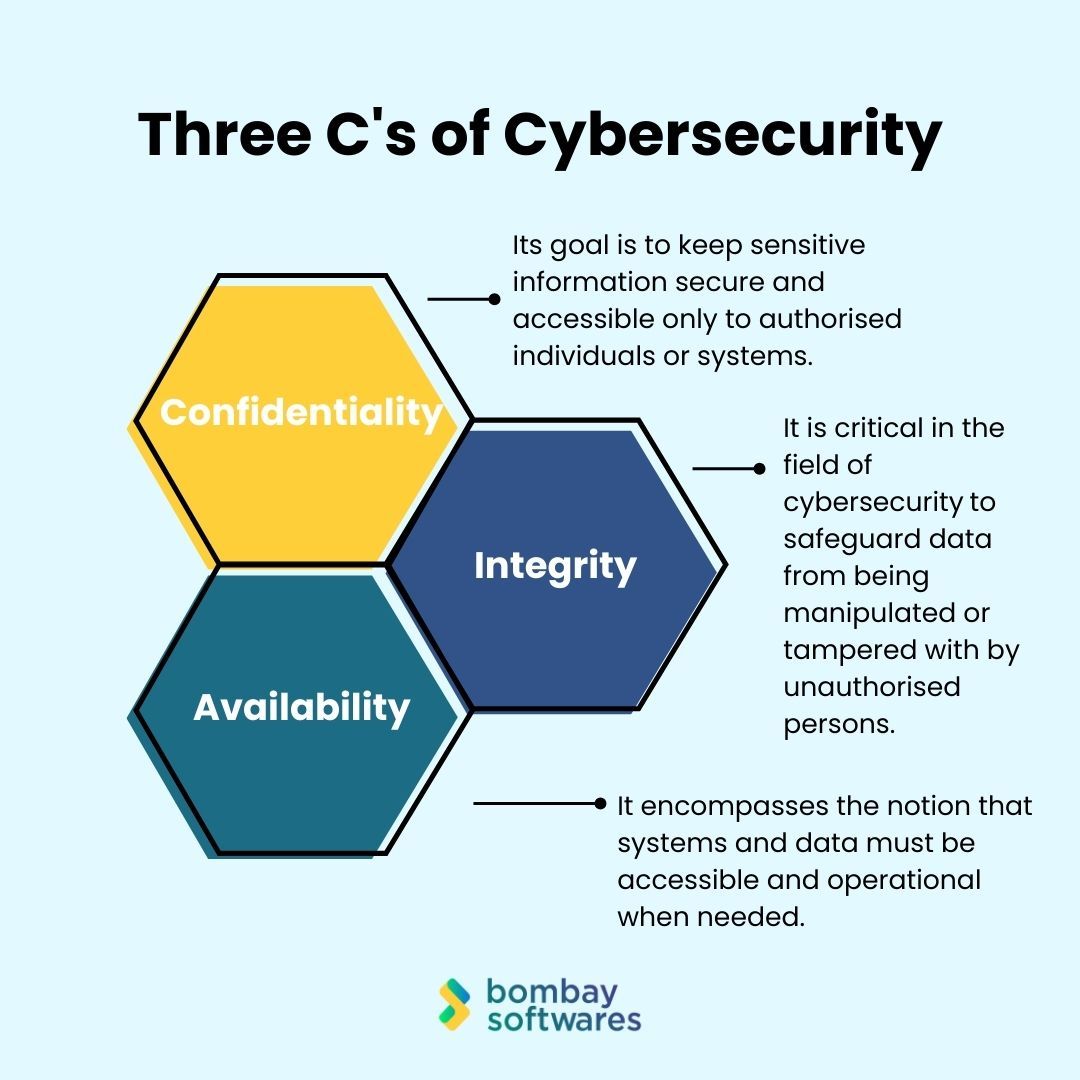
1. Confidentiality
The foundation of cybersecurity is confidentiality. Its goal is to keep sensitive information secure and accessible only to authorised individuals or systems. To achieve this, encryption plays a pivotal role.
Encryption techniques transform data into unreadable code, which can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key.
Whether it's personal data, financial records, or classified government information, maintaining confidentiality is crucial to prevent unauthorised access and data breaches.
2. Integrity
The dependability and accuracy of data are referred to as integrity. It is critical in the field of cybersecurity to safeguard data from being manipulated or tampered with by unauthorised persons.
Data integrity is upheld through various mechanisms, including checksums, digital signatures, and data validation processes. Ensuring the integrity of data safeguards its reliability and maintains its value and trustworthiness.
3. Availability
Availability is the third pillar of the Three C's. It encompasses the notion that systems and data must be accessible and operational when needed.
Cyberattacks often target the availability of critical systems through Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, for example, which flood network programs with traffic to overwhelm and disrupt services.
Maintaining availability involves robust backup systems, redundancy, and failover mechanisms to mitigate downtime and ensure uninterrupted access to resources.
4 Key Principles of Cybersecurity
To effectively address the Three C's and safeguard against cyber threats, cybersecurity strategies are guided by four key principles:
1. Govern: Identifying and Managing Security Risks
The governance aspect of cybersecurity involves establishing a framework to identify, assess, and manage security risks.
It encompasses creating policies, procedures, and guidelines to guide security best practices. Effective governance ensures that cybersecurity is integrated into an organisation's overall strategy.
2. Protect: Implementing Security Controls
The "Protect" principle is about putting safeguards in place to mitigate security risks. This involves implementing various security controls, such as firewalls, encryption, access controls, and security cyber awareness training. Protecting systems and programs data is vital to prevent breaches and unauthorised access.
3. Detect: Identifying Cybersecurity Incidents by Detecting and Understanding Cybersecurity Events
Detecting cyber threats in a timely manner is essential to minimising damage. This principle involves setting up monitoring systems and intrusion detection tools to identify abnormal activities or potential security breaches.
Rapid detection enables organisations to respond effectively.
4. Respond: Cybersecurity Incident Response and Recovery
Inevitably, despite preventative measures, security incidents can occur. The "Respond" principle focuses on having an incident response plan in place.
It outlines how an organisation should react when a breach occurs, from isolating affected systems networks to notifying stakeholders and law enforcement. A well-prepared response can limit the impact of an incident.
The 7 Layers of Cybersecurity
Imagine cybersecurity as a fortress with multiple layers of defence, each playing a crucial role in protecting sensitive information and digital infrastructure.
The "Seven Layers of Cybersecurity" idea encapsulates these defence mechanisms, giving a comprehensive method for mitigating risks and protecting against a wide range of attacks.
1. Physical Security
The first layer of cybersecurity is physical security. This involves safeguarding the physical infrastructure that supports your digital assets. This includes secure data centres, access control, surveillance, and measures to protect against natural disasters or physical intrusions.
2. Network Security
Network security focuses on safeguarding the pathways through which data travels. This layer involves firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to protect data in transit. It's akin to securing the highways of the digital world.
3. Perimeter Security
Perimeter security establishes a virtual barrier around your network, often through firewalls and intrusion prevention systems. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network devices traffic to prevent unauthorised access and attacks.
4. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is concerned with the protection of individual devices such as PCs, cellphones, and tablets. It involves installing antivirus software, conducting regular updates, and implementing security policies to prevent malware and other threats.
5. Application Security
Applications are a common target for cyberattacks. This layer involves securing software and applications through secure coding practices, penetration testing, and continuous monitoring for vulnerabilities.
6. Data Security
Data is one of the most valuable assets. Data security encompasses encryption, access controls, and data backup strategies to protect sensitive information from unauthorised access, theft, or corruption.
7. Cloud Security
With the adoption of cloud computing, cloud security has become crucial. It involves securing data, applications, and services hosted in the cloud, often through identity and access management, encryption, and monitoring.
Types of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not a one-size-fits-all concept; it comprises various types, each designed to counter specific threats:
1. Network Security
Network security focuses on securing the communication pathways between devices and systems. It includes technologies like firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems.
2. Information Security
Information security emphasises the protection of data and information assets. This encompasses data encryption, access controls, and data classification.
3. Application Security
Application security is concerned with securing software and applications against vulnerabilities and threats. It includes secure coding practices, penetration testing, and code analysis.
4. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is dedicated to safeguarding individual devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Antivirus software, encryption, and intrusion detection systems are key components.
5. Cloud Security
Cloud security addresses the unique challenges of cloud computing, including data security, identity management, and compliance within cloud environments.
6. IoT Security
Internet of Things (IoT) security involves safeguarding the vast array of interconnected devices, from smart thermostats to industrial sensors. It ensures the security and privacy of the data exchanged between these devices.
7. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is crucial for controlling and managing user access to networks, systems, and applications. It involves authentication, authorization, and privileged access management.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is the protector of our digital existence in our digital age, where the barriers between the physical and digital worlds are blurring. It is not only a technical issue; it is a basic requirement to safeguard our privacy, financial assets, key infrastructure, and, ultimately, our way of life.
It is essential to understand the importance of cybersecurity, its key principles, and the seven layers of defence. Recognising the different types of cybersecurity strategies and how they may be used to protect against specific threats is also essential.
As we continue to embrace the benefits of information technology, we must also embrace our responsibility to protect the digital world.
More blogs in "Cybersecurity"
- 6th Nov, 2023
- Arjun S.
Digital Trust: The Backbone of E-commerce Success
- 25th Dec, 2023
- Rohit M.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Trends And Predictions For 2025
Join our Newsletter
Get insights on the latest trends in technology and industry, delivered straight to your inbox.









